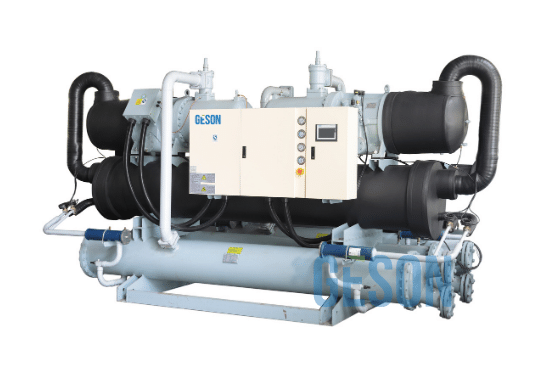
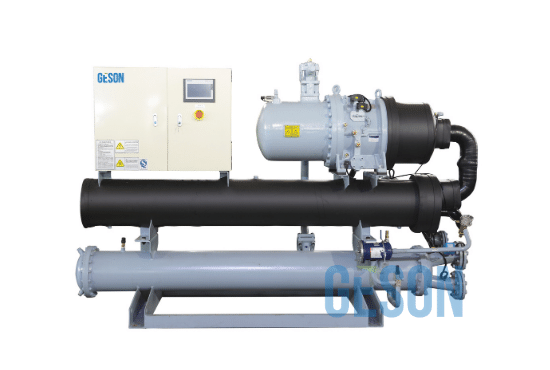
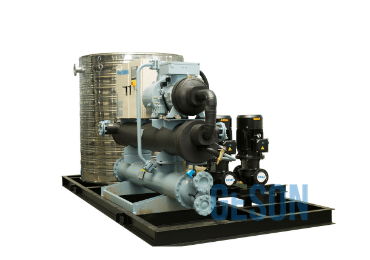
GESON Chiller System
Your Best Chiller System Solution
Are You Looking for Chiller System for Your Industrial Processing Cooling?
1. The chiller system can be divided into a low-temperature chiller system
and a normal temperature cooling water system in terms of temperature control.
The temperature of the room temperature cooling water system is generally controlled within the range of 5℃-35℃,
The temperature control of the low-temperature chiller system is generally 5°C and below
2. In terms of equipment type, it can be divided into integrated cooling water chiller systems and split cooling water chiller systems.
The split cooling water chiller system, mainly used for cooling high-power instruments and equipment,
and its water circulation system and refrigeration chiller system are installed indoors and outdoors respectively
3. In terms of equipment power, it is divided into a small cooling water circulation chiller system and a large cooling water circulation chiller system (water-cooled chiller unit).
Small cooling water circulation chiller system, low cooling power, suitable for cooling a single device
Large-scale cooling water circulation chiller system (water-cooled unit), suitable for large-scale unit cooling
4. From the type of compressor, it is divided into DC start-stop cooling water circulation chiller system and frequency conversion energy-saving cooling water
circulation chiller system.
Geson chiller system is a perfect choice in humid and dusty environment areas.
Adopts the best suitable compressor, according to the project site need.
Customize the cooling capacity, chilled water temperature, refrigerant types, and voltage type.
You can make your industry at a stable working and lowest cost.
Main Products
- Chilled water temperature 5~25℃
- Refrigerant types: R22/R134A/R407C/R410A and etc.
- Compact in structure, cover small area, save machine room space.
- Cooling capacity ranges: 30~4500RT
- Loading adjusted 100%, 75%, 50%, 25%,0.
- Completely running tested before the delivery from the factory.
- Cooling capacity ranges: 10HP~80HP
- Built-in a water tank and water tank
- Easy for maintenance and service.
- The scroll compressor is long-life operating and easy to maintain.
All Types of Industrial Water Chiller Products
Modular Air Chiller
Who We Are?
If you are finding the industrial chiller system for your process system.
Geson water chiller systems can meet all your varies of requirements.
Here, you will have the ultimate economical solution.
From the professionally experienced R&D team, you will satisfy the industrial water chiller system.
We can supply the following types of water chiller systems:
- Screw Chiller Systems
- Centrifugal Chiller Systems
- Rotary Screw Chiller Systems
- Scroll Chiller Systems
You can get the following services:
- Customize chiller types, compressor types.
- Precious chilled water temperatures.
- The most suitable economical refrigerant.
- The OEM brand for your brand.
- Stable operation with 40000 hours failure-free.
- Customize the voltage as your need.
Contact our engineer, to get the right solution for your industry.
Advantages of Geson Chiller
We want to be your expert chiller manufacturer in China
Top Brand Components
Ensure Your Top Quality Chiller
Applications

Chiller For Plastic Industrial

Beer And Wine Fermentation Chiller

Chemical Processing Chiller

Computer Data Center Chiller

Food And Dairy Chiller

Hotel HVAC Chiller

MRI And Laser Chiller
Pharmaceutical-Formulation-chiller

Swimming-Pool-chiller
Ultimate FAQs: Refrigeration Cooling Water Chiller Systems | Geson Chiller
This information will help you in getting the best Chiller System.
Indeed, it identifies everything.
That you have been searching for.
Hence, it includes version, kind, advantages, price, and maintenance, among other important points.
So before you buy a Chiller System, go through this guide.

air cooled chiller system
· What is a Chiller System?
A chiller is an appliance that absorb heat from a fluid through different principles.
Thus, they include adsorption refrigeration, vapor-compression, or absorption refrigeration cycles.
Moreover, this fluid can then be transferred via a heat exchanger to cool equipment.
It can be carried out by another method stream (such as air or process water).

Figure 1 A Chiller System
· What are the Main Functions of a Cooling Chiller System?
The cooling system assists three essential functions.
First, it removes heat from the engine.
Second, it retains the engine performing temperature where it works most effectively.
Finally, it develops the engine to the accurate operating temperature as quickly as possible.

Figure 2 Functioning of a Chiller System
· What are the Two Basic Kinds of Chiller Systems?
There are two kinds of cooling systems.
They are:

water cooled chiller system
In this kind of cooling system, the heat, which is removed to the outer parts of the engine.
It is radiated and conducted away by the stream of ambient air.
Thus, it is received from the environment.

air chiller system
· What are the Components of the Cooling System?
The following are some significant components of a cooling system.
- Cooling Fan
- Radiator
- Water Pump
- Thermostat
- Hoses
- Antifreeze/Coolant

chiller components
· What are the Four Main Components in a Refrigeration System?
The refrigeration cycle contains four major components.
They are:
- Compressor
- Condenser
- Expansion device
- Evaporator
Refrigerant remains piped between these four items.
Moreover, it is present in the refrigerant loop.
The refrigerant commences as a cold vapor and moves to the first component.
i.e., the compressor.

Figure 3 Main Components of a Refrigeration System
· How do you Maintain a Chiller System?
The followings are some tips to consider regarding maintenance of a Chiller System:
- Keep a daily check:
The daily assessment is still the foremost step towards retaining an effectively-run chiller plant.
This assists you to create a history of performing conditions.
These include:
- Temperatures
- Pressures
- Fluid levels
- Flow rates.
- Keep tubes clean for effective heat transfer:
Heat transfer efficiency has the most significant single effect on chiller execution.
So clean heat transfer is a primary component to retaining high efficiency.
Moreover, condenser tubes should be brush cleaned at least annually.
Thus, to keep them free of pollutants.
- Operate condenser water to prevent scale, corrosion
Assess chilled water loops once a year or regularly with remote monitoring.
Subsequently, for the usual water quality and evidence of corrosion.
- Lessen entering liquid temperature
Lowering the temperature of the entering condenser liquid will enhance the chiller’s efficiency.
However, on some systems, the executor will lower the chilled water set point.
Thus, to get rid of air handler deficiencies such as dirty coils.
- Sustain adequate refrigerant charge
The amount of cooling a chiller supplies depends on how much refrigerant it circulates through the compressor.
Thus, it is essential to retain the exact level of refrigerant for the desired conditions.
However, refrigerant leaks, as well as air and moisture introduce into the system, will decrease efficiency and the stability of the system.
Moreover, a low refrigerant charge will cause the compressor to perform harder for less cooling effect.
Ø Try to Avoid Inefficiencies Caused by Non-condensable
Non-condensable such as air and moisture leak into low-pressure chillers because their evaporators perform in a vacuum.
Moreover, Non-condensable can decrease the real stability of the chiller.
However, purge units lower the impact of non-condensable.
- Check the operation of starters and motors.
Assess the safety and sensor calibrations on microprocessor controls.
Subsequently, for the adequate performance of starters and motors.
Then, assess electrical connections, wiring, and switchgear.
Consequently, which are associated with the chiller for hot spots and worn contacts.
- Install variable speed drives
The chiller motor is usually the most considerable single electrical load in a building.
Thus, with accurate performing conditions, variable speed drives (VSD) can provide significant energy savings.
Thus, varying motor speed matches motor effectivity to load and wastes less energy.
· What is the Chiller Set Point?
A water chiller usually performs with a set point of 50°F or higher.
However, if setpoints between 20°F – 48°F are needed?
Thus, special measures must be taken to avoid freezing and possible hazard.
Moreover, attention must be given to freeze protection, water supply and pressure swath limit reconciliations.

Chiller Temperature Setting
· What is the Safety Operation in the Chiller System?
Each chiller wants a different setting that corresponds to the load for maximum effectivity.
Moreover, every chiller generally has safety modulators that are created to protect the cooling system from harm.
Such as low refrigerant temperature, low oil pressure, or high condensing pressure.
· What is the best Chiller Efficiency?
Maximum chiller effectivity is providing the most significant tonnage at the lowest kilowatt use.
However, maximum effectivity occurs with most chillers operating at approximately 70-75 percent load.
Thus, the lowest entering condenser water temperature (ECWT), depending on the design.
· How can we enhance the Capability of the Water Chiller System?
There are three ways to increase Chiller Efficiency.
They are:
- Consider variable speed retrofits:
Most parts within a chilled water system will benefit from variable speed drives.
- More is less: Performing various parallel devices optimizes savings.
Chiller plant component generally works more efficiently at part-load.
- Ascend supply temperatures.
· Why does a Water Chiller System Trip?
A Chiller System may trip due to the following reasons:
- Low pressure
- Low refrigerant
- Power assembly has broken capillary.
- Low or no water movement
- Blocked water filter or screen
- Coolant or mud coating the tubes of the evaporator causing poor performance.

chiller boiler system
· How do you troubleshoot a Water Chiller?
Following are some necessary measures which can help troubleshoot the problem:
- Ensure that the chiller is working.
Your chiller may stop working due to a blown circuit breaker or fuse.
Moreover, loose wiring or merely a power switch that’s might put in the “off” position. It might also stop the chiller from running.
- Make sure whether the chiller is cooling.
Thus, assess the temperature of the coolant at the chiller’s outlet to the process.
If it isn’t at or near the preferred temperature?
The evaporator might get freezes.
However, it is also possible that the heat transfer properties of the coolant fluid might be declining.

Figure 4 Chiller Troubleshooting
· How do you reset your chiller system?
Here’s the link to a video.
That tells how to reset your Chiller system:
· How Do you Lower the Power Consumption of Your Chiller System?
A chiller with a same-speed compressor motor reacts to a reduced load.
Moreover, it lowers the entering condenser water temperature by closing its vanes.
Thus it lessens the flow of refrigerants saves some energy.

chiller and cooling tower system
· What is the Function of the Economizer in the Chiller System?
An economizer is a kind of sub-cooler that uses a portion of the total refrigerant flow from the condenser.
Thus, to cool the rest of the refrigerant flow.
Hence, the cold gas from the economizer can also be used to supply extra cooling for the compressor.

Figure 5 An Economizer in a Chiller
· Which Water is used in the Chiller System?
Glycol-Water Mixture is used in the chiller system.
Using Glycol for inner applications is also suggested as it deters scale and corrosion in the device.
Moreover, it supplies some oil to the chiller pump while protecting metals.
However, external applications require more Glycol.
It depends on the maximum low ambient the chiller may see.
· How is the Chiller Load Calculated?
The typical sizing formula is as follows:
- Measure Temperature Differential (? T°F)
- MeasureBTU/hr. BTU/hr.
- Calculatetons of cooling capacity Tons = BTU/hr. ÷ 12,000.
- Oversize the chillerby 20% Ideal Size in Tons = Tons x 1.2.
- You have the perfect size for your requirements.
· What is a COP for the Chiller System?
COP stands for Coefficient of Performance.
Thus, it indicates the efficiency of heating and cooling appliances.
Moreover, the COP is defined by the ratio of heat dissipation and electrical power intake.
Hence, it’s like the ability of the machine, but higher than 100%.
Thus, it could be less than 100% for a machine not working accurately.

chiller system diagram
· How Much Energy Does a Chiller Use?
It has been approximated that motors and pumps used in chillers consume 10,737 MWh of electric energy for different percentage of loadings.
As chillers are significant energy users, variable speed drives are applied in chillers.
Thus to lessen their energy consumption.

chiller system design
· What is Chiller Surge?
Chiller surge is a situation in which refrigerant moves in reverse from the condenser back to the compressor.
Thus, it can cause severe destruction.
Hence, pressure builds up in the compressor, causing the refrigerant to surge forward again.
Thus the cycle repeats.

Figure 6 Chiller Surge
· How do You Stop a Surge Chiller?
Here’s the link to a video.
That tells how to avoid a chiller surge.
· Can Chillers be Used for Heating?
A typical chiller can be used in heat-recovery applications.
However, most standard water-cooled chillers can give suitable condenser water temperatures for heat recovery.
If executed at a slightly high refrigerant condensing temperature (e.g. 105°F).
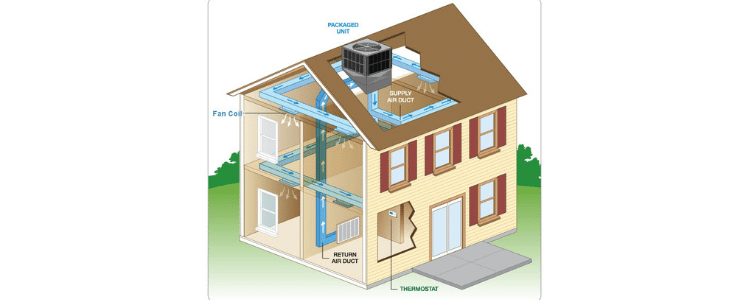
chiller system for home
· What is a Chiller System Overhaul?
A chiller teardown and overhaul involve taking your chiller apart.
Thus, assessing parts, replacing critical components as required, and putting it all back together.
Moreover, by overhauling your chiller, technicians can point out problem areas that are otherwise difficult to spot.

Figure 7 Chiller Overhaul
· What is VGD in Chiller System?
The modern invention gives a variable geometry diffuser (VGD) principle.
Thus the VGD principle may be used to reduce compressor backspin.
Moreover, related transient loads during compressor shut down by avoiding a reverse flow of refrigerant gas.
Through the diffuser gap during compressor shutdown.
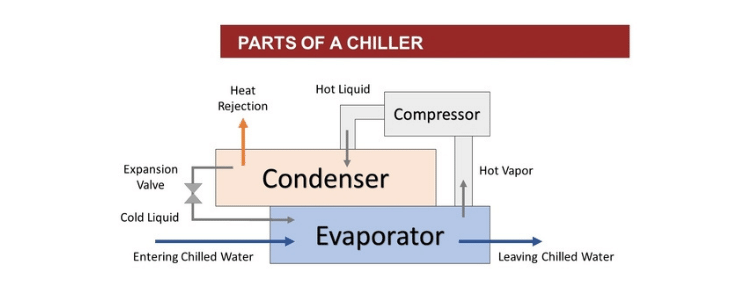
chiller system components
· How Much Pressure is in a Chiller System?
General pressures close to the plant change from 5 to 30 psi.
However, far from the plant, they may change from 2.5 to 10 psi.
However, the pipe to valve size ratio is generally mentioned as the “piping geometry factor”.

chiller plant system
· What Causes High Head Pressure in a Chiller System?
Most high head pressure problems will be on the condenser side of the system.
The component usually on the roof or outdoor.
However, one of the primary faults is the physical fouling of the condenser fins.
Thus, it stops airflow over the coils.

chiller plant management system
· Why is Glycol Used in the Glycol Cooling System?
Using Glycol in your glycol cooling system chiller may prove to be valuable.
Thus, Glycol decreases the freezing point of the process liquid.
Moreover, it ensures that it continues to circulate at a precise temperature.

chiller machine
· Is Glycol Dangerous?
Ethylene glycol is chemically decomposed in the body into harmful components.
However, it and its hazardous byproducts first harm the central nervous system.
Afterward, the heart, and finally, the kidneys.
Moreover, the ingestion of large amounts can be dangerous.

Refrigerant Is Used In a Water Cooled Chiller System
· Which Gas is Used in the Chiller System?
Chillers used to chill industrial operations.
They are included under the group of “industrial process refrigeration”.
Thus, applicable refrigerants for this application are R-410A, R-404A, R-407C, and R-134a.
However, these gases are accepted on all chillers systems.
Moreover, it offers a broad extent of employment chances.
The business can also be very supportive and might mean little or no student liability.
Chiller System is positively recognizing for those who want a profession that doesn’t need staying at the desk daily.
Now chiller systems are widely used in the refrigeration and refrigeration industry, and the refrigerant is usually R22 (also R134a). In order to facilitate operation and maintenance and reduce the installation location, the refrigeration compressor, oil separator, water-cooled shell and tube condenser, filter drier, solenoid valve and other components are usually installed on the same base to form a compression condensing unit. The reuse pipeline is connected to the evaporator through the expansion valve to form a complete refrigeration system.

absorption chiller system
Normal operating conditions in the operation of the refrigeration system:
- The suction temperature of the compressor should be 5-15℃ higher than the evaporation temperature.
- The exhaust temperature of the compressor R22 system shall not exceed 150℃.
- The maximum oil temperature of the compressor crankcase shall not exceed 70°C.
- The suction pressure of the compressor should correspond to the evaporation pressure.
- The discharge pressure of the compressor R22 system shall not exceed 1.8MPa.
- The oil pressure of the compressor is 0.12-0.3MPa higher than the suction pressure.
- Always pay attention to the amount of cooling water and water temperature. The outlet water temperature of the condenser should be 2-5°C higher than the inlet water temperature.
- Always pay attention to the oil level of the compressor crankcase and the oil return of the oil separator.
- The compressor should not have any knocking sound, and the heat of all parts of the body should be normal.
- The condensing pressure shall not exceed the discharge pressure range of the compressor.

chiller ac system
The discharge temperature of the compressor is too high:
- The suction pressure is too low, the suction and exhaust pressure difference is too large (the cylinder compression ratio is large), the opening degree of the expansion valve is small, and the adjustment pressure is low.
- The suction temperature is too high, that is, the suction is overheated, the suction pipe is too long or the heat preservation effect is poor.

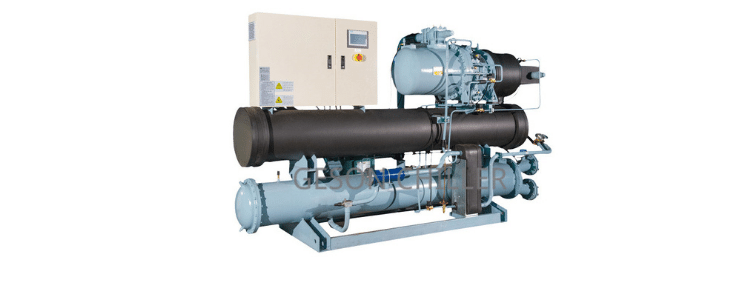
Industrial Water Cooled Screw Chiller Application
- The amount of cooling water is insufficient or the water temperature is too high.
- Too much non-condensable gas (air) in the system.
- The condensing pressure is too high, and the corresponding condensing temperature is also high, causing the exhaust temperature to rise.
- The compressor cylinder or valve group is faulty.

how chiller works with diagram
The discharge pressure of the compressor is too high:
- Too much non-condensable gas (air) in the system.
- The amount of cooling water is insufficient or the water temperature is too high.
- The condenser is too dirty and has too much scale.
- Too much refrigerant in the system.

how chiller system works
The oil temperature of the compressor is too high:
- The suction and discharge temperature of the compressor is too high.
- The lubricating oil is too dirty or the oil quality is too bad
- The compressor parts are severely worn.
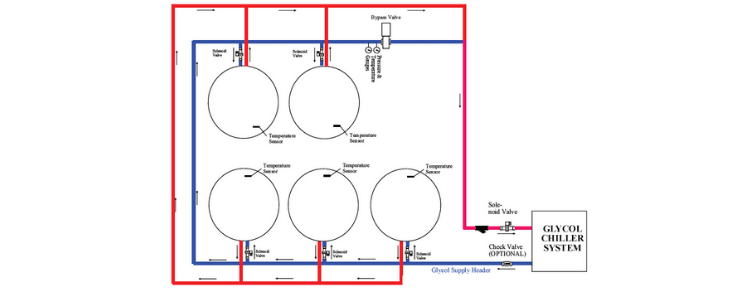
glycol cooling system
Condensing pressure and condensing temperature are too high:
- The condenser cooling water is insufficient or the water temperature is too high.
- The condenser is too dirty and has too much scale.
- Too much non-condensable gas (air) in the system.
- Too much refrigerant in the system.
- The heat transfer area of the condenser is configured too small.
water cooled chiller
Frequently check and master the operating conditions of the refrigeration system, eliminate operating faults, eliminate abnormal phenomena at any time, and carefully and carefully adjust the system in the best state. It is very important for the safe, normal and economic operation of the refrigeration system. It is the inspection of the operators. The fundamental standard of technical quality and sense of responsibility.